 |
 |
|
|
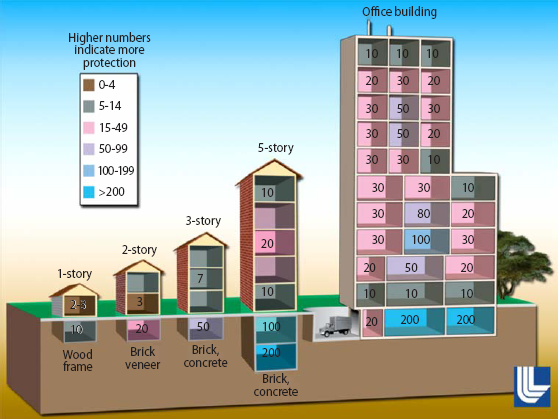
| Example protection factors (PFs) for a wide variety of building types and locations.
|
|
- Numbers represent a "dose reduction factor".
- A dose reduction factor of 200 indicates that a person in that area would receive 1/200th of the dose of a person out in the open.
Source: Key Response Planning Factors for the Aftermath of Nuclear Terrorism (PDF - 4.52 MB) (Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory, August 2009, Page 12, Figure 9)
Buildings provide considerable protection from fallout
- A brick building provides better protection from radiation than does a brick veneer building, which is better than that of a frame building.
- Less radiation exposure (increasing the Protection Factor) is seen at interior locations and below ground.
- The multiple-story office building illustration below shows that the middle floors provide better shielding than the ground floor or exterior locations because fallout that emits gamma radiation covers the ground, exterior surfaces, and the rooftop.
- Moving to a higher floor in the building increases the distance from the ground source but increases exposure from radiation on the rooftop.
Reference:
Sheltering in Place During a Radiation Emergency (HHS/CDC, May 2006)
|



