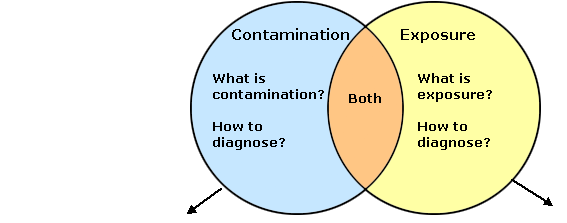
Differences Between Contamination and Exposure
Contamination:
Replay animation

Replay animation
- Contamination results when a radioisotope (as gas, liquid, or solid) is released into the environment and then ingested, inhaled, or deposited on the body surface.
-
How to diagnose:
-
External contamination
- Scan with appropriate radiation survey meter
-
Internal contamination
- Swab each nostril separately to help estimate level of internal (lung) contamination
- If after external decontamination, an appropriate radiation survey meter continues to identify significant residual radioactivity, suspect internal contamination.
- Collect ≥70 mL spot urine sample for isotope measurement
- Consider total body radiation survey with modified hospital nuclear medicine equipment
-
External contamination
Exposure:
Replay animation

Replay animation
-
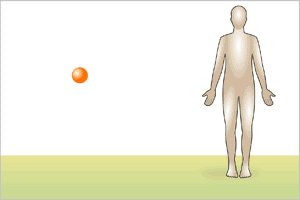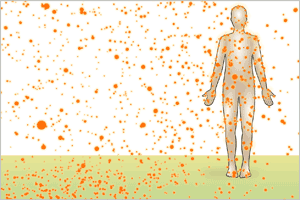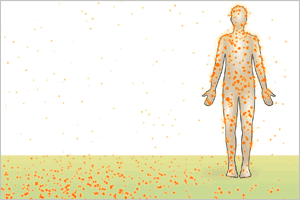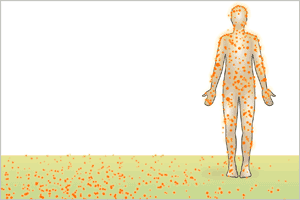
Radiation exposure occurs when all or part of the body
absorbs penetrating ionizing radiation from an
external radiation source, as shown in the illustration
above.
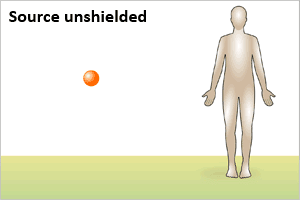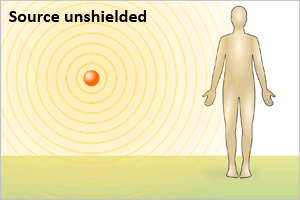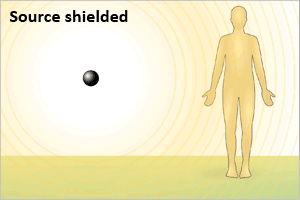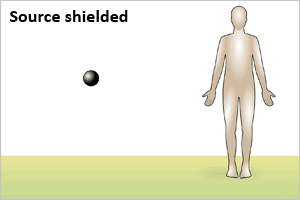
- Exposure from an external source stops when a person leaves the area of the source, the source is shielded completely, or the process causing exposure ceases.
-
Radiation exposure also occurs after internal
contamination, i.e., when a radionuclide is ingested,
inhaled or absorbed into the blood stream.
- This kind of exposure stops only if the radionuclide is totally eliminated from the body, with or without treatment.
- An individual exposed only to an external source of radiation, as shown above, is NOT radioactive or contaminated and may be approached without risk, just like after a chest x-ray or CT scan.
-
Radiation from external exposure alone is either absorbed
without the body becoming radioactive, or it can pass
through the body completely.
- Therefore, if a person is scanned with a radiation survey monitor after external exposure alone, the device will not register radiation above the background level.
- Acute Radiation Syndrome (ARS) may result if the dose from whole or partial body exposure is high enough.
- How to diagnose ARS: estimate whole body dose and clinical severity by using

